How to Build a Preventive Maintenance Checklist to Protect Your Business Assets
Blog

Table of Contents
Take Control of Your Assets
A personalized demo is just one click away.
It’s easy to take business assets for granted, but they play a critical role in daily operations and overall success. In the broadest sense, “assets” include everything from office equipment, furniture, and facilities to company vehicles, IT hardware, and even intangible assets like data and institutional knowledge. Protecting these assets through regular upkeep is one of the most effective ways to safeguard your bottom line. One proven strategy is to implement a preventive maintenance checklist that ensures all assets receive timely care before problems arise.
What Is Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance refers to scheduled, proactive maintenance on your business assets to prevent breakdowns and costly repairs. In other words, it’s the practice of servicing and inspecting assets on a routine basis to maximize their lifespan and avoid disruptive downtime.
Instead of waiting for equipment to fail and then fixing it, preventive maintenance means planning maintenance tasks at regular intervals. This might include activities like lubricating machinery, updating software on IT systems, replacing wear-and-tear parts, and performing safety inspections. By keeping to a planned schedule, you address minor issues before they escalate, ensuring vital equipment doesn’t suddenly break down and halt productivity.
Which Business Assets Need Preventive Maintenance?
Nearly every physical asset in a business can benefit from preventive care. Among the most common assets requiring routine maintenance are:
- Facilities and Building Systems: This includes your physical office buildings or warehouses, HVAC units, electrical systems, elevators, and plumbing. Regular inspections of your facilities (e.g., roof checks, HVAC filter changes, etc.) can prevent small issues like leaks or mechanical strain from becoming major problems.
- Machinery and Equipment: In manufacturing or construction, machines and tools need scheduled servicing such as lubrication, calibration, and parts replacement. For example, factory equipment might have a maintenance schedule for oiling moving parts or changing belts to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- IT Hardware and Electronics: Computers, servers, networking equipment, and other IT assets benefit from cleaning (to prevent overheating due to dust), software updates, and hardware checks. A preventive maintenance checklist for IT might involve running security updates, backing up data, and testing power supplies or battery backups.
- Vehicles and Fleets: Company cars, trucks, and other vehicles require routine oil changes, tire rotations, brake inspections, and more. Keeping a log of each vehicle’s mileage and service dates helps ensure transportation assets remain safe and reliable.
- Safety Equipment and Gear: Items like fire extinguishers, emergency generators, alarms, and personal protective equipment (e.g., helmets, gloves, etc.) need periodic checks. Ensuring fire suppression systems are charged and safety gear is in good condition protects employees and complies with safety regulations.
By identifying all your assets and their maintenance needs, you can prioritize tasks and allocate resources effectively. Remember that preventive maintenance isn’t just for heavy machinery – from office printers to facility infrastructure, proactively maintaining all the items your business relies on ensures smooth operations.
How to Build a Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Every organization should create and follow a preventive maintenance checklist tailored to their unique assets and industry requirements. If you’ve never used one before, consider the following best practices when building your checklist:
1. List All Assets and Schedule Service Intervals
Begin by documenting all your assets that need maintenance. For each asset, determine how often it requires service (e.g., daily, monthly, quarterly, annually, etc.). This information might come from manufacturer recommendations or industry standards. For example, HVAC systems need filter changes every 3 months, fleet vehicles need oil changes every 5,000 miles, and servers might need updates monthly.
2. Track Service History
For each asset on the checklist, include a space to log past repair or maintenance activities and dates. Keeping a service history helps you identify patterns (e.g., a machine that frequently needs repair might be due for replacement) and ensures that nothing is overlooked. A quick glance at the history will tell you when the last service was done and when the next one is due.
3. Monitor Condition and Lifespan
Your checklist should prompt you to assess the overall condition of the asset during each maintenance cycle. Include checkpoints like “inspect for wear and tear” or “check operating temperature”. Over time, these notes help predict the asset’s remaining useful life and improve your business’s overall lifecycle management. For instance, if a vehicle’s checklist notes show tires nearing tread limits, you can plan to replace them in a timely manner.
4. Keep an Inventory of Parts and Supplies
Good preventive maintenance includes having the right replacement parts and tools on hand. This requires accurate, real-time inventory. On your checklist, note any parts that need regular replacing (e.g., filters, belts, batteries, etc.) and ensure that your maintenance team knows where to find these parts or how to order them. This prevents delays – maintenance can be done on schedule when all necessary pieces are available.
5. Include Data Backup and Software Updates
If your assets include computers or digital systems, your preventive maintenance checklist should cover backing up important data and updating software or firmware. For example, a checklist for a server might include “Backup database – Weekly” and “Install security patches – Monthly”. This step ensures that digital assets are also protected against failure or cyber threats.
6. Regularly Review and Update the Checklist
A maintenance checklist is not a static document. Schedule periodic reviews—say annually or whenever you acquire new assets—to update the list. Add new equipment, remove retired assets, and adjust maintenance intervals based on experience. If a certain machine showed unexpected issues, you might increase its check frequency. Keep the checklist flexible so it remains relevant as your business grows or changes.
By following these steps, you create a living maintenance document that guides your team. The checklist template can be as simple as a spreadsheet or as advanced as a module in maintenance management software – what matters is that it’s clear, accessible, and consistently used.
Best Practices for Improving Preventive Maintenance
Starting a preventive maintenance program can feel overwhelming, but a few best practices can guide you to success. Whether you’re tracking a handful of assets or managing thousands, consider these expert tips:
Document Your Assets
Begin with an up-to-date inventory of all business assets, including relevant details such as make/model, serial numbers, locations, purchase dates, and warranties. You can’t maintain what you don’t know you have. A complete asset register is the foundation for scheduling and tracking maintenance.
Identify Risks and Prioritize
For each asset, determine what risks or vulnerabilities it faces. Is it prone to overheating? Does it operate in a harsh environment? Prioritize maintenance for high-risk and mission-critical assets first. For example, a high-value machine that will stop production if it fails should have more frequent checks than a seldom-used piece of equipment.
Schedule Regular Checks (and Stick to Them)
Consistency is key. Use calendars or maintenance software to plan out routine inspections and service tasks. Whether it’s daily vehicle tire inspections or quarterly facility safety audits, schedule them and assign responsibility. Treat these maintenance appointments as non-negotiable, just like you would an important meeting or client deadline.
Carry Out Inventory and Stock Checks
Regularly audit spare parts, consumables, and tools needed for maintenance. Part of preventive care is ensuring you have the supplies to perform tasks. Running out of printer toner or lacking a replacement fan belt when needed can delay maintenance and lead to asset downtime. Keep a checklist for inventory management so that parts are reordered in advance.
Implement Access Controls and Security
Protect certain assets by limiting who can use or handle them. For instance, sensitive data should only be accessible to authorized personnel, and expensive machinery might require trained operators. Preventive maintenance isn’t only mechanical – it includes policies that reduce misuse or overuse. Proper usage and storage of assets will naturally decrease the wear and tear they experience.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Many industries have legal maintenance requirements (such as health, safety, or data protection laws) that are imperative to incorporate into your checklist. For example, include tasks like “Verify fire extinguishers are certified annually” or “Test emergency lighting monthly” to remain compliant and avoid penalties. Compliance-driven maintenance tasks often protect both assets and people.
Continuously Review and Improve
Conduct regular reviews of your maintenance practices. If an asset still failed despite preventive measures, analyze why. Maybe the maintenance frequency should increase, or the procedure needs adjusting. Also review if your maintenance activities are actually preventing issues as intended. Use metrics like breakdown frequency or maintenance costs over time to gauge effectiveness and adjust your strategy.
Train Your Team
Lastly, make sure the people involved in maintenance are well-trained and understand the importance of the checklist. A checklist is only as good as its execution. Train staff on how to perform each task correctly and why it matters. Encourage a culture where employees report anomalies (e.g., unusual noises, warning lights, etc.) so they can be addressed proactively.
Asset Panda: Your Preventive Maintenance Partner
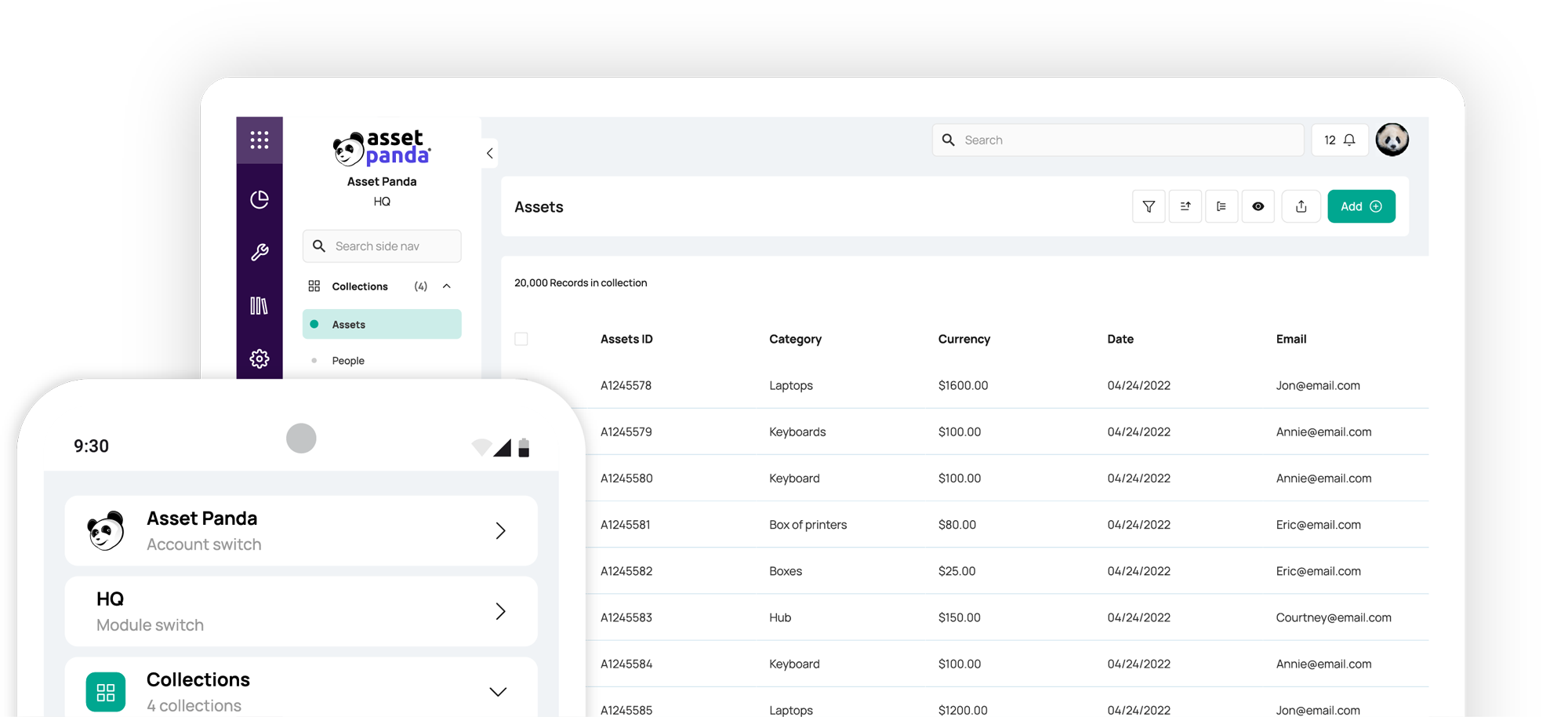
Managing a comprehensive maintenance program can be complex, especially as your organization grows. This is where maintenance management software comes into play. Asset Panda’s powerful yet user-friendly platform is designed to support your preventive maintenance efforts and protect your business assets.
With Asset Panda, you can track each asset’s maintenance schedule, service history, and warranty information all in one place. The software sends automatic reminders for upcoming maintenance tasks, so nothing falls through the cracks. It also allows you to attach photos, manuals, and checklists to each asset’s profile for easy reference.
By using Asset Panda to digitize your preventive maintenance checklist, you eliminate guesswork and ensure consistency. The result is fewer unexpected breakdowns, streamlined audits and compliance reporting, and greater peace of mind.
Schedule your personalized demo today to see how Asset Panda can streamline your preventive maintenance efforts.
Take Control of Your Assets
A personalized demo is just one click away.
[addtoany]
Related News & Press
Learn more from a solution specialist
Schedule a demo to find out how you can transform your workflows with Asset Panda Pro
Contact our team at (888) 928-6112